文章最后更新时间:2023-09-13 13:34:34,由管理员负责审核发布,若内容或图片失效,请留言反馈!

《动手学深度学习》,一起动手,学习深度学习。
目录
第一章 介绍
1.1 介绍1.2 常用数据集1.3 第一个例子第二章 基础
2.1 Dense层2.2 激活函数2.3 数据标准化(Normalization)2.4 丢弃(Dropout)2.5 优化器2.6 损失函数2.7 卷积计算2.8 LeNet第三章 进阶
3.1 深层神经网络AlexNet3.2 深层神经网络ResNet3.3 深层神经网络EfficientNet待续2.4 丢弃法(Dropout)
丢弃法,是添加Dropout层并指定丢弃概率。在训练模型时,Dropout层将以指定的丢弃概率随机丢弃上⼀层的输出元素;在测试模型时,Dropout层不发挥作⽤。
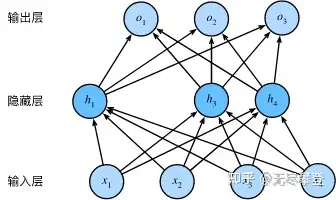
图1来源于《Dive into Deep Learning》,图 3.5 隐藏层使用了丢弃法的多层感知机,https://zh-v1.d2l.ai/chapter_deep-learning-basics/dropout.html
2.4.1 神经网络
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
import os
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
# 安装 scikit-learn
# pip install sklearn -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
from sklearn import manifold, datasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ====================================
# 神经网络
# ====================================
def build_sequence_network(dim, feature_dim=100, num_classes=10, dropout_rate=0.1, normalization=None):
# 输入层
if normalization == batch:
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.Input(shape=(dim,), name=input_layer),
BatchNormalization(name=batch_norm),
Dropout(rate=dropout_rate),
Dense(feature_dim, activation=tanh, name=feature_layer),
Dense(num_classes, name=task_layer, activation=softmax),
]
)
elif normalization == layer:
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.Input(shape=(dim,), name=input_layer),
LayerNormalization(name=layer_norm),
Dropout(rate=dropout_rate),
Dense(feature_dim, activation=tanh, name=feature_layer),
Dense(num_classes, name=task_layer, activation=softmax),
]
)
else:
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.Input(shape=(dim,), name=input_layer),
Dense(feature_dim, activation=tanh, name=feature_layer),
Dense(num_classes, name=task_layer, activation=softmax),
]
)
# 优化器和损失函数
model.compile(optimizer=adam,
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name=Accuracy))
# 模型汇总
model.summary()
return model
2.4.2 例子
# 训练轮次
epochs = 10
# 批次数量
batch_size = 128
# 加载数据
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 形状由(60000, 28, 28),改为(60000, 768)
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (x_train.shape[0], -1))
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (x_test.shape[0], -1))
# ==============================
# 模型训练
# ==============================
norm_names = [None, batch, layer]
accuracy_list = []
val_accuracy_list = []
for rate in [0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]:
model, encoder = build_sequence_network(dim=x_train.shape[1], normalization=layer, dropout_rate=rate)
History = model.fit(x_train,
y_train,
shuffle=True,
epochs=epochs,
batch_size=batch_size,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
accuracy_list.append(History.history[Accuracy])
val_accuracy_list.append(History.history[val_Accuracy])
# ===========================================
# 显示训练集、验证集准确率
# ===========================================
plt.clf()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 5))
dropout_rates = [0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]
for rate, acc, val_acc in zip(dropout_rates, accuracy_list, val_accuracy_list):
# 显示训练集准确率
y = acc
x = np.array(range(epochs), dtype=np.int)
ax.plot(x, y, label=Dropout_{}.format(str(rate)))
# 显示坐标轴名称
ax.set_xlabel(Epochs)
ax.set_ylabel(Accuracy)
ax.set_title(Normalization)
ax.legend()
figure_path = ./figures
if os.path.exists(figure_path) is False:
os.makedirs(figure_path)
plt.savefig(os.path.join(figure_path, network_dropout_mnist_accuracy.png))
plt.clf()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 5))
for rate, acc, val_acc in zip(dropout_rates, accuracy_list, val_accuracy_list):
# 显示验证集准确率
y = val_acc
x = np.array(range(epochs), dtype=np.int)
ax.plot(x, y, label=Dropout_{}.format(str(rate)))
# 显示坐标轴名称
ax.set_xlabel(Epochs)
ax.set_ylabel(Accuracy)
ax.set_title(Normalization)
ax.legend()
plt.savefig(os.path.join(figure_path, network_dropout_mnist_val_accuracy.png))
2.4.3 分析
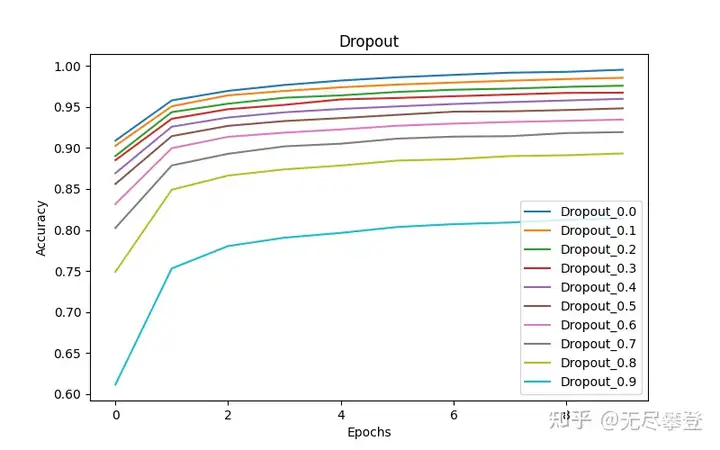
从图1训练集的准确率来看,随着Dropout的比率越来越高,准确率越来越低,到了05以后开始加速下降。
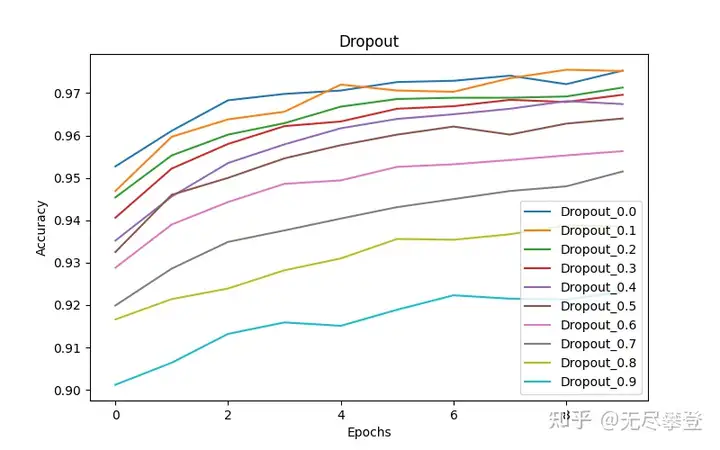
从图2验证集的准确率来看,也是随着Dropout的比率越来越高,准确率越来越低,到了0.5以后开始加速下降。
Dropout的比率在0.5以下,可能是比较合适的。
参考文献
Sergey Ioffe, Christian Szegedy. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167Jimmy Lei Ba, Jamie Ryan Kiros, Geoffrey E. Hinton. Layer Normalization. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450联系我们
如果您有任何意见和建议,请随时联系我们。
公众号: AI-for-Sci

文章版权声明:除非注明,否则均为信达升级网原创文章,转载或复制请以超链接形式并注明出处。




